Deadweight loss also known as excess burden is a measure of lost economic efficiency when the socially optimal quantity of a good or a service is not produced.
Deadweight loss price floor government buys surplus.
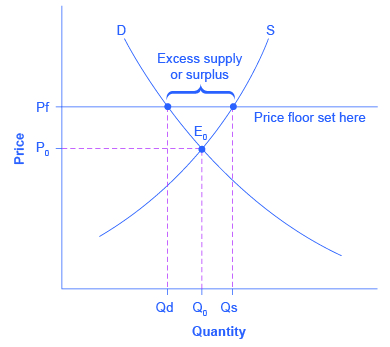
Figure 4 6 shows the demand and supply curves for the almond market.
The cost to the government of the price support is equal to the cost of the surplus in the market represented in gray.
Description of how price floors operate in a competitive market and the effects on consumer surplus producer surplus and social surplus using supply and dem.
Percentage tax on hamburgers.
Refer to figure 4 6.
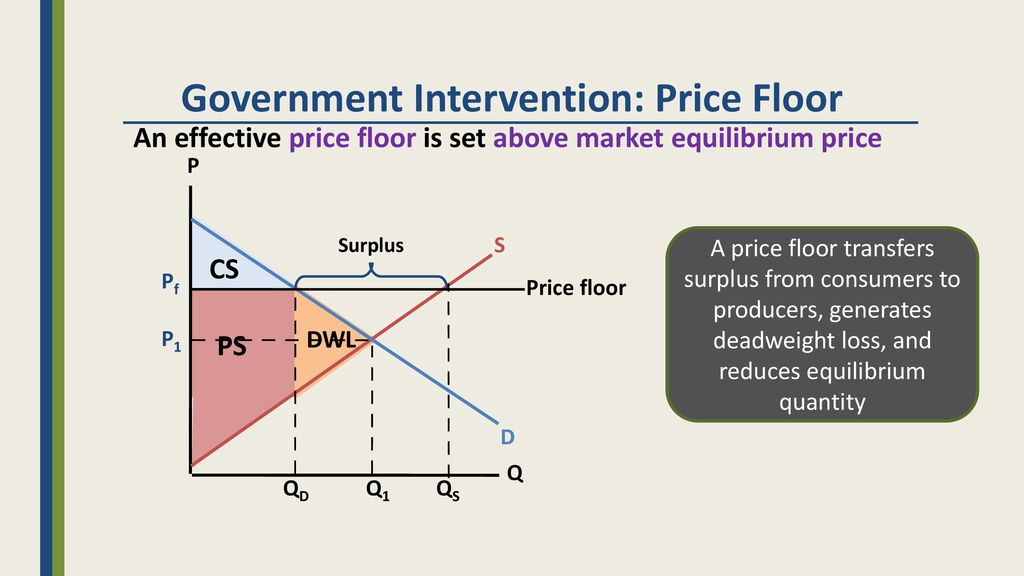
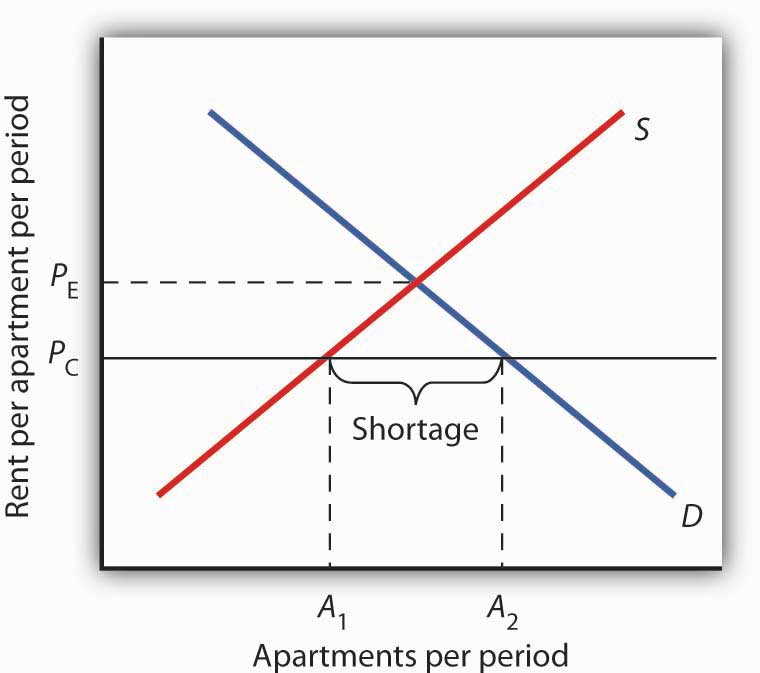
The government sets a limit on how low a price can be charged for a good or service.
Taxes and perfectly inelastic demand.
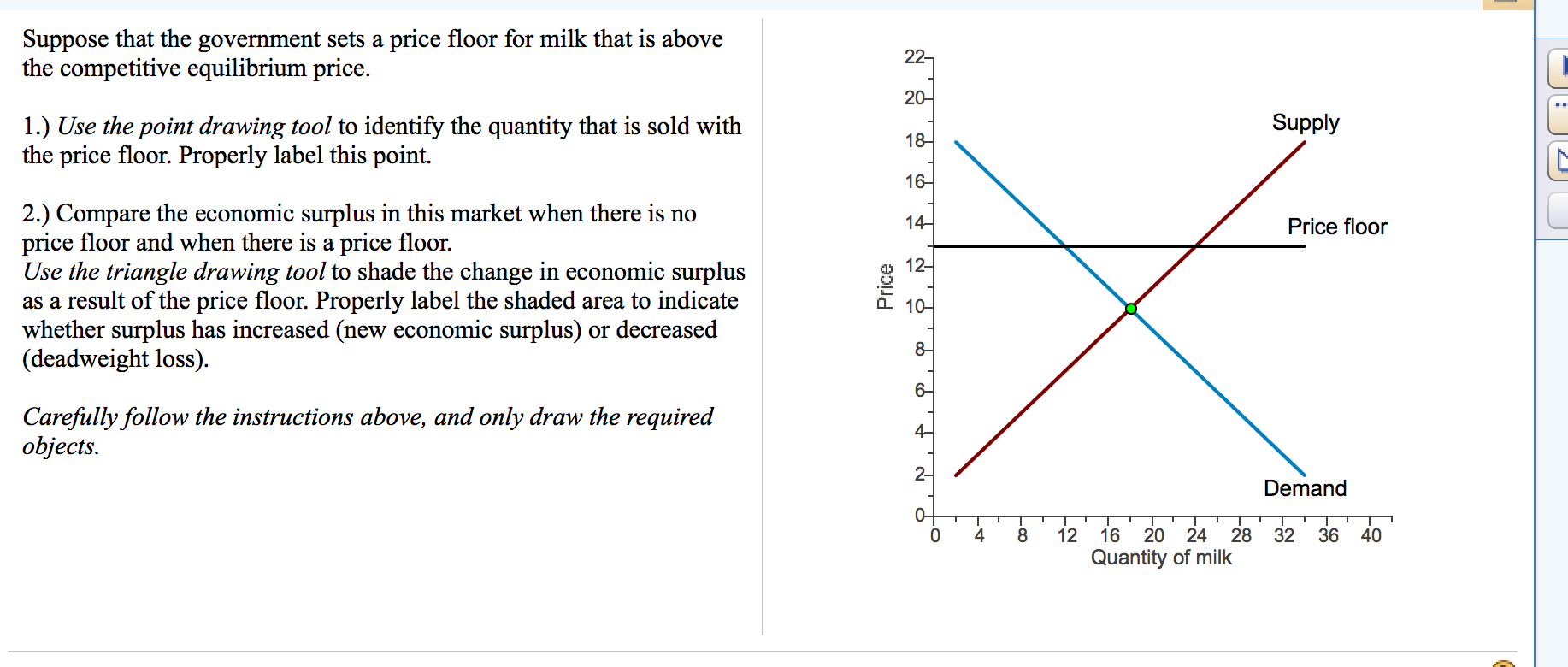
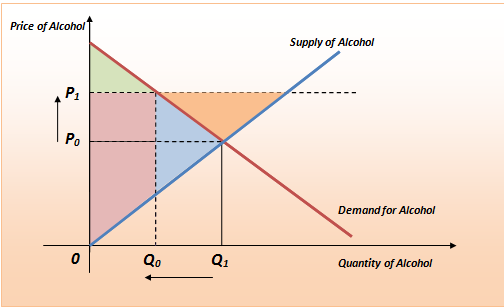
What area represents the deadweight loss after the imposition of the price floor.
6 200 1200 however since the consumers ultimately pay taxes for the government to purchase the surplus the total cost to consumers in the short run of the price support is the sum of the loss in consumer surplus and.
D a deadweight loss triangle whose corners are cde.
A a deadweight loss triangle whose corners are abc.
The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor.
An example of a price floor would be minimum wage.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
B a deadweight loss triangle whose corners are acd.
Practice what you have learned about the impact of prrice controls and quotas on consumer surplus producer surplus total surplus and deadweight loss in this exercise.
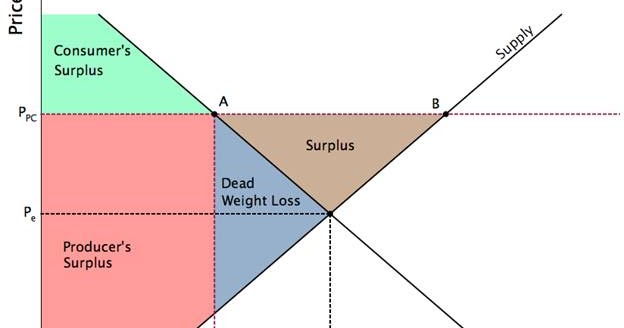
Causes of deadweight loss.
A price floor of p1 causes.
Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers.
B excess supply equal to the distance ab.
A excess demand equal to the distance ab.
A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at.
Minimum wage and price floors.
If you re seeing this message it means we re having trouble loading external resources on our website.
The government believes that the equilibrium price is too low and tries to help almond growers by setting a price floor at pf.
Deadweight loss sometimes called efficiency loss occurs when economic surplus is not maximized.
An example of a price ceiling would be rent control setting a maximum amount of money that a landlord can.
Non optimal production can be caused by monopoly pricing in the case of artificial scarcity a positive or negative externality a tax or subsidy or a binding price ceiling or price floor such as a minimum wage.
C a deadweight loss triangle whose corners are bec.
How price controls reallocate surplus.
It can be caused by price floors price ceilings excise taxes noncompetitive markets or negative and positive externalities.
The effect of government interventions on surplus.